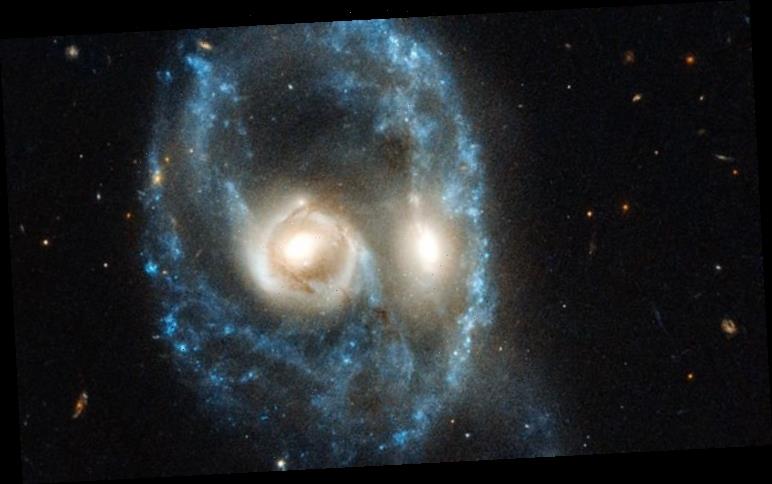
US-based space agency NASA has released its latest Hubble picture depicting a pair galaxies resembling glowing eyes glaring menacingly at Earth. NASA described in a statement how “the piercing eyes are the most prominent feature of what resembles the face of an otherworldly creature. They said: “But this is no ghostly apparition. Hubble is looking at a titanic head-on collision between two galaxies.”
Each “eye” is in fact the luminous core of a galaxy, one of which slammed into another 704 million light-years from Earth.
This is no ghostly apparition. Hubble is looking at a titanic head-on collision between two galaxies
NASA
The apparent outline of the eerie “face” is a ring of young blue stars, while other clumps of new stars form a nose and mouth.
The entire system, photographed in June, is identified as Arp-Madore 2026-424 (AM 2026-424), from the Arp-Madore Catalogue of Southern Peculiar Galaxies and Associations.
Although galaxy collisions are common, especially back in the early Universe, most of them are not head-on smashups, such as this collision.
The violent cosmic encounter gave the system an arresting “ring” structure for a relatively short period of time, about 100 million years.
The collision contracted and stretched the galaxies’ disks of gas, dust and stars outward.
This action formed the ring of intense star formation shaping the nose and face.
Ring galaxies are rare, with only a few hundred of them residing in Earth’s cosmic neighbourhood.
DON’T MISS
Asteroid danger: 100% certainty of impact warns space expert [INTERVIEW]
Hubble snaps galaxy ‘like a portal to another dimension’ [PICTURES]
What is the mysterious dark vortex NASA found on Neptune? [ANALYSIS]
READ MORE
-
X-37B: Secretive spaceplane returns to NASA after 780 days in orbit
The galaxies have to collide at exactly the right orientation to create the ring.
The galaxies will merge completely in about 1 to 2 billion years, hiding their violent past.
The side-by-side juxtaposition of the two central bulges of stars from both galaxies also is unusual.
Because the bulges creating the eyes appear to be the same size, it suggests two galaxies of approximately equal proportions were involved in the crash, rather than more common collisions where small galaxies are devoured by their larger neighbours.
NASA’s Hubble Space Telescope observed this unique system as part of a “snapshot” program that takes advantage of occasional gaps in the telescope’s usually busy observing schedule to gain additional photographs.
Astronomers plan to use this innovative Hubble program to take a close look at many other unusual interacting galaxies.
The intention is to compile a robust sample of nearby interacting galaxies, to gain insight into how galaxies develop through galactic mergers.
After analysing these detailed Hubble images, astronomers will then decide which systems are prime targets for extra analysis with NASA’s James Webb Space Telescope, scheduled to launch in 2021.
Source: Read Full Article