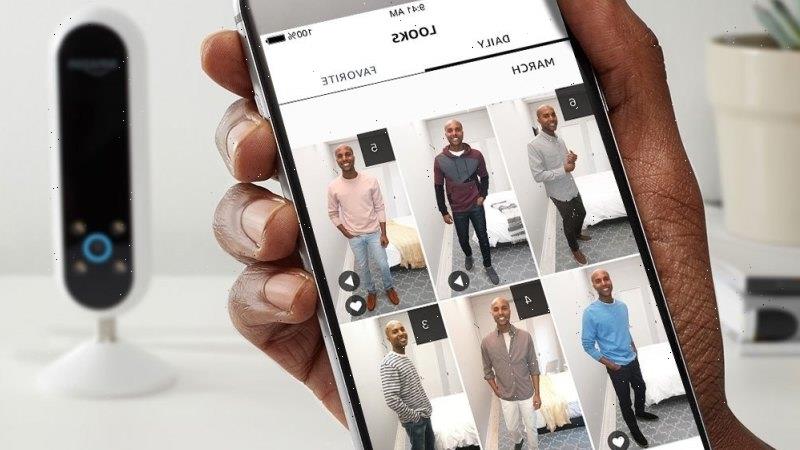
About four years ago, Paul Hollowell found out that Amazon was making a gadget he desperately wanted: a camera whose sole purpose was to photograph his clothes.
The oval camera, called the Echo Look, worked by photographing several clothing combinations and using artificial intelligence to highlight which outfit looked best. Hollowell, an entrepreneur and a frequent traveller based in the US, usually spent hours picking clothes to pack for a trip and believed that the camera would help him decide. He ordered one for $US200 ($263).
Amazon discontinued its Echo Look camera and app last year.Credit:Amazon
He was correct; the camera saved time. But what he didn’t predict was that Amazon would send an email three years later with sad news: The product and its app would soon cease to work. The company said it had included some of the Echo Look’s features, like giving style advice, in more popular Amazon products, so it was time to put the digital fashionista to rest.
Hollowell, 39, was angry.
“You can sunset the service, but at least let me use the camera,” he said. “It just did nothing.”
Many have learned a hard lesson about what it means to be an Amazon customer. Even when you’re paying lots of money, you are a guinea pig at the whims of a company endlessly striving to innovate. At any moment, the company could surprise you with an unwelcome change to an Amazon product you own or decide to kill it altogether.
Last week, many Americans who own Amazon devices were automatically enrolled in Sidewalk, a new internet-sharing program that drew intense scrutiny. Basically, the program lets owners of newer Amazon products share their internet connections with others nearby. If a neighbor’s Ring camera has a spotty internet connection and yours has a strong one, you can share your bandwidth with your neighbour.
That all sounds nice if everything works as expected, but security experts have raised concerns that device makers could have inappropriate access to people’s data. They advised that people opt out of the program to avoid becoming part of Amazon’s experiment because there are still many unknowns.
This high-risk, high-reward approach to innovation is woven into Amazon’s culture. Jeff Bezos, the company’s founder, has said that Amazon’s failures cost it billions of dollars. He once told investors that his company was “the best place in the world to fail (we have a lot of practice!), and failure and invention are inseparable twins.”
Indeed, Amazon’s unbridled embrace of failure has included high-profile flops in consumer electronics. For about four years it sold millions of Amazon Dash Buttons in the US, which you could push to replenish items like toilet paper. Amazon killed the Dash in 2019, after orders placed through the buttons significantly decreased. In 2014 the company aggressively marketed the Fire, its first smartphone, and shelved it just a year later amid lukewarm reviews and sluggish sales.
This high-risk, high-reward approach to innovation is woven into Amazon’s culture. Jeff Bezos, the company’s founder, has said that Amazon’s failures cost it billions of dollars.Credit:AP
Amazon continues to experiment with kitschy ideas. Last year it unveiled an autonomous drone that flies around your home and shoots video to catch intruders. The drone, which was widely panned by the press because of privacy concerns, has yet to be released. Halo, a US-only fitness product that Amazon claims can tell you precisely how fat you are, received mixed ratings from professional reviewers and early customers, including complaints that the gadget could give people body dysmorphia.
Why does Amazon, a brand that probably knows more about what Americans want to buy than any other company, need to sell experimental products just to figure out what it’s doing? Tech companies big and small typically do their research and development in house before releasing products.
What’s more, when Amazon fails like this, customers, the guinea pigs, lose hard-earned cash and a product they may enjoy. There is also an environmental impact: The electronic device could end up in a landfill, and even if it’s recycled, only a small portion of its materials can be reused.
Lisa Levandowski, an Amazon spokeswoman, said that internal teams tested the company’s inventions extensively but that, because they were novel and ambitious, customer feedback could help improve them. This approach allows Amazon to make products like the Echo and Alexa what they are today, she said.
Why does Amazon, a brand that probably knows more about what we want to buy than any other company, need to sell us experimental products just to figure out what it’s doing?
Design veterans with experience creating products for Big Tech brands like Apple and Samsung confirmed that Amazon’s method was atypical. My general recommendation is to think twice before buying cutting-edge tech products made by Amazon; and if you do, be aware of the risk.
Slow and steady vs. on-the-fly innovation
A television, no matter how thin, makes an ugly centrepiece in a living room once it’s turned off. With this in mind, Yves Béhar, a Swiss designer, teamed with Samsung to design a TV that could blend into the room like an art piece, he said.
They took a slow and patient approach.
Béhar said he and Samsung designers had started with making observations about consumers: Homes were getting smaller, and tastes were becoming more eclectic. With that insight, the product developers worked with curators in museums and galleries to assemble art that could be shown on the TV.
After a few years of testing prototypes and forming partnerships to procure artwork, the collaboration resulted in the 2017 introduction of the Frame TV, a Samsung television that resembled a picture frame. It used motion sensors to show art when people were present and shut off when nobody was around. The TV has become a bestseller.
Béhar, who founded Fuseproject, an industrial design firm, said he understood Amazon’s approach as a retail company to rapidly test ideas; like when it measures how customers respond to different prices in its stores. But “with hardware, people end up being left with stuff that’s useless or doesn’t work anymore,” he said. “In the world that we live in today, with global warming and plastics and waste, I do think it’s something to be very careful about.”
Hollowell is an example of how tough it can be to pacify unhappy customers. When Amazon was announcing the death of the Echo Look, the company sent two emails. The first included a promotional code to get a newer product, the Echo Show 5, for free. Hollowell took the offer but found that the Echo Show was a poor substitute: The camera was subpar and lacked software to organise his closet, he said.
The second email was a reminder that the Echo Look would soon be dead and that it could be recycled. Hollowell missed the part about recycling.
“I very distinctly remember putting it in the trash one day because it just wasn’t working,” he said.
The New York Times
Get news and reviews on technology, gadgets and gaming in our Technology newsletter every Friday. Sign up here.
Most Viewed in Technology
From our partners
Source: Read Full Article