Charging space agencies to launch satellites into orbit is the drastic measure proposed by scientists to deal with the worsening space debris problem. University of Colorado Boulder researchers believe international consensus is required in order to charge space agencies “orbital use fees” for each satellite.
The amount charged would increase each year to 2040 up to £200,000 ($235,000), according to the team.
Space is a common resource, but companies aren’t accounting for the cost their satellites impose on other operators
Professor Matthew Burgess
This is in order to cover the significant costs of preventing catastrophe.
The team claim by charging an annual fee for every satellite put in orbit, agencies would have an incentive to remove them once they become obsolete.
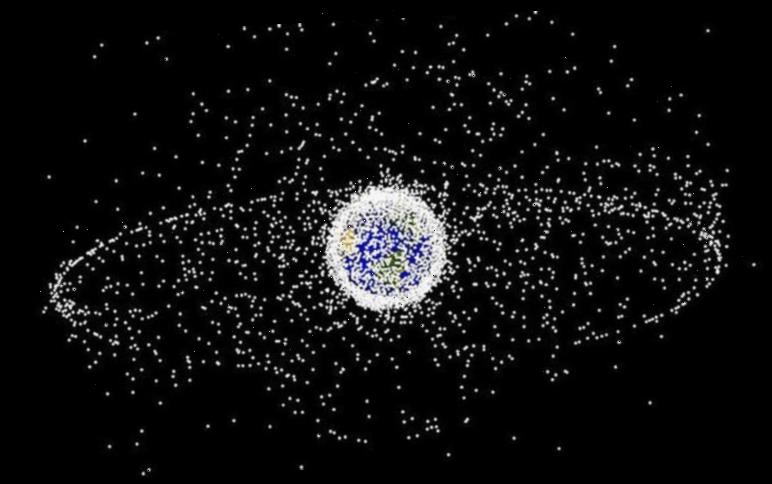
Approximately 20,000 objects, such as satellites and space detritus are crowding low-Earth orbit, meaning a collision between man-made objects could create thousands of small pieces.
Proposals to deal with the space junk problem have focused on technology or management.
READ MORE
-
NASA news: New comet SWAN spotted by space agency’s Solar Observatory
However, the latest research suggests financial incentives may be more effective.
Introducing fees may reduce the number of satellites placed in orbit and lead to more satellites being taken out of orbit as organisations look to slash costs.
Professor Matthew Burgess, an economist and co-lead author of the paper, said: “Space is a common resource, but companies aren’t accounting for the cost their satellites impose on other operators when they decide whether or not to launch,’ said .
“We need a policy that lets satellite operators directly factor in the costs their launches impose on other operators.
Orbital-use fees could be straight-up fees or tradable permits, and they could also be orbit-specific.
This is because satellites in different orbits produce varying collision risks.
The resulting fee for each satellite would be calculated to reflect the cost to the industry of putting another satellite into orbit.
This would include projected current and future costs of additional collision risk and space debris production.
DON’T MISS…
SpaceX Starlink: Exact times and dates to see Starlink [INSIGHT]
Space quiz questions and answer for your home quiz [QUIZ]
NASA unveils plan to stop a deadly virus from landing on Earth [INSIGHT]
READ MORE
-
Elon Musk teases a bold plan to terraform Mars with 10,000 nukes
These are costs operators not currently factored for by space agencies.
Professor Daniel Kaffine, the study’s co-author, said: “In our model, what matters is that satellite operators are paying the cost of the collision risk imposed on other operators.”
Fees would increase over time, to account for the rising value of cleaner orbits.
In the researchers’ model, the optimal fee would annually rise at a rate of 14 percent, reaching approximately £200,000 ($235,000) per satellite-year by 2040.
The researchers also announced , all countries launching satellites would need to take part for such an orbital-use fee approach to work.
Approximately a dozen nations launch satellites independently launch vehicles, while more than 30 launch their own satellites.
In addition, each country would need to charge the same fee per unit of collision risk for each satellite that goes into orbit, said the research team.
Similar approaches are already made in carbon taxes and fisheries management.
In this study, the team compared orbital-use fees to business as usual – open access to space – and to technological fixes such as removing space debris.
Source: Read Full Article